While the majority of Joplin’s lead and zinc mines were below ground, and in fact, much of Joplin is built above those shafts, there were some that were open to daylight. Below is a photograph of one of the best examples, the aptly named Daylight Mine.
“Young Men Are Dying” – Frances Perkins’ visit to Joplin
On April 23, 1940, a crowd of two hundred people stood on the train platform at Joplin’s Frisco Depot, awaiting the arrival of an important visitor to the city. Many of them would have identified themselves as union representatives, but their visitor was not famed labor leader John L. Lewis, head of the United Mine Workers. Instead, when passengers began to disembark from the train, the individual who captured the crowd’s attention was a woman, often described by her contemporaries as “plain,” perhaps even ordinary looking. Plain and ordinary she was not. Frances Perkins, U.S. Secretary of Labor, was the first woman appointed to a position in the U.S. Cabinet. In response to the epidemic of “miner’s lung” in the Tri-State Mining District, Perkins convened a conference known as the Tri -State Silicosis Conference to allow concerned citizens, representatives from mining companies, government officials, and union representatives to discuss the issue.
Among those waiting at the platform to greet Perkins were Evan Just, secretary of the Tri-State Zinc and Lead Ore Producers Association; Frank Evans, president of the association; and the Reverend Cliff Titus, representing the Joplin Chamber of Commerce. Perkins then headed to the Connor Hotel where she stayed during the duration of the conference. She held a five minute press conference in which she stated that the purpose of her visit “is because you have silicosis there, and the labor department is concerned in preventing and correcting conditions due to silicosis.” After the press conference concluded, Secretary Perkins then headed outside to board a specially chartered bus. Together she and thirty other individuals representing various interests toured the mining district. Traveling out of Joplin on Route 66, she sat at the front of the bus with Tony McTeer, the district CIO president, and Evan Just. While driving past squalid miner’s shanties, Secretary Perkins remarked that something needed to be done to help those living in such dire circumstances.
The first stop was at the St. Louis Refining and Smelting Company’s Ballard Mine near Baxter Springs, Kansas. Secretary Perkins donned a “miner’s metal hat, raincoat, and overshoes” before she descended 350 feet into the mine where she then watched demonstrations of different mining methods. She was reportedly very interested in the “methods used by miners in drilling and in a dust control demonstration” given by Fred Netzeband, air hygiene engineer of the Tri-State Zinc and Lead Ore Producers Association. Secretary Perkins was later quoted by an observer as saying, “The world should know the true picture of methods being used in controlling and eliminating dust in the mines.”
After the demonstration, she then met with several of the miners, shook their hands, and listened to their views of the different methods used to control dust. Perkins was accompanied twenty other interested individuals, including Episcopal Bishop William Scarlett of St. Louis; the Reverend Charles Wilson of St. Mark’s Episcopal Church in St. Louis; and Miss Elizabeth Wade White of New York. All three were members of the Tri-State Survey Committee. It was perhaps the one and only time that a bishop of any religious denomination toured one of the Tri-State District’s mines.
Secretary Perkins then visited Treece, Kansas, and Hockerville and Picher, Oklahoma to view housing conditions. In Treece, she visited the home of Mr. and Mrs. William Hannon. Hannon and two other former miners told Perkins that they suffering from silicosis and were unable to receive treatment. Hannon’s wife and four children also reportedly suffered from silicosis. She then met with six women, described as the widows of miners, who stated that they and their children were plagued by silicosis. Secretary Perkins’ bus did not stop in Hockerville and Picher, but she was reportedly able to view “slum conditions” in all three towns from her bus seat. She then returned to the Connor Hotel and prepared for the conference which began at 2 o’clock in the afternoon. The conference itself was held on the roof of the Connor.
The conference revealed a variety of attitudes. After making her opening remarks, Secretary Perkins was followed by the Reverend Cliff Titus. Titus, appearing as a “representative of the public,” declared that workers in the Tri-State Mining District were all white, not foreigners; and that “they are independent and prefer to choose their own methods of living.” He then continued “Many of our people prefer to live near chat piles because they want to spend their money on other things” like cars. But Titus acknowledged that “people of the district are willing and anxious to bring about better living conditions in the mine sections and will co-operate with state and federal agencies.”
Evan Just, secretary of the Tri-State Zinc and Lead Ore Producers Association, spoke on behalf of a majority of mine operators. He declared that operators had made great strides in reducing silicosis over the last several years. Just cited statistics that allegedly showed that incidences of silicosis in miners had been reduced from 60 percent in 1913 to 22 percent in 1929. Further progress, he claimed, had been in the years since. What Just failed to mention, however, is that this only applied to the large mining companies who could afford modern mining equipment, and not the smaller independent operators who could not. Just, however, denied that individuals could contract silicosis from surface dust.

Miner shacks from the turn of the century - the condition of miners' homes continued to be poor decades later.
He then addressed living conditions in the Tri-State Mining District by stating that slum conditions were the result of social problems. “That many people who can afford better homes prefer to live in small, unpainted two and three-room shacks and spend their surplus funds on automobiles and radios cannot be charged against the mining industry,” Just maintained, although he claimed the mining industry did want to eliminate squalid living conditions. He was followed by representatives from federal and state public health, relief, and labor agencies. Even former Joplin resident Mrs. Emily Newell Blair, the noted political activist, was in attendance. Notably, former miner and the district CIO president, Tony McTeer, spoke in the interests of miners. He said, in part:
“Madam Secretary, ladies and gentlemen, conferences as such are not new to you, and to many people it is the usual approach to a problem, to sit down with all interested parties and discuss what is wrong in order to agree on a remedy. I can frankly tell you that a conference of this sort is new and different to the working people of the Tri-State area…
Some people believe that because the miners have not made a lot of noise about their troubles, because of the ignorance of themselves and others, that the workers have no troubles. That is not correct.
I am proud of our miners here. They know they have troubles aplenty, and what they are, but they also know false hopes when they see them. They have been fooled too often, so that now they don’t let themselves in for another deception.
However, they also know a good beginning when they see it. And this conference was received by the people of the Tri-State with great hope and anticipation of beneficial results…
We appreciate your coming this long distance, knowing that you would be convinced that here lies a serious problem.
Young men are dying. Ailing mothers and sick little children arouse in you the interest you have shown by being here today. Our district has the greatest percentage of widowhood in the United States; a sad commentary. These are the things that must be stopped for the future welfare of all the citizens who live here.
The problem as we see it is threefold. First, dust control; second, proper hospital facilities; third, adequate housing.
To reduce the high death rate among the miners requires better dust control and better working conditions in the mines. Stopping silicosis is one step in the direction of curbing the infection of tuberculosis. Mines today go in for more mechanical equipment, as we are living in a world of progress. I haven’t myself worked in a mine for the last five years, but the mining conditions and the health of the miners are my business. Our people working in the mines today give many exact reports of what does on in the mines.
It is said that wet drilling has solved the problem of dust control.
There have been two general fields of mining in this district. First, what we term the old country, which is the Joplin, Webb City area. Second, the Oklahoma and Kansas mining district. In the Joplin district the drilling was done with the piston machine or dry drills. The water liner drilling machine was introduced into Oklahoma and Kansas fields in 1916 or 1917, and from around that period it has been used exclusively. I wish to speak from my own experiences on this. I have never worked in mines except where water-lined drills were used, and I have silicosis, or dust on my lungs. We can produce the names of hundreds of men who have never worked except under wet drilling conditions, and we have buried a great many of them. I have prepared a list of some of those men who I know have died. I am turning it, with my statement, over to the chairman of this meeting.
Since wet drilling alone does not solve the problem, the problem still is dust control. We must get at the root of the problem…”
At the end of the conference, the Tri-State Survey Committee of New York sponsored a showing of “Men and Dust,” a short documentary film by noted photographer Sheldon Dick. Dick had journeyed to the Tri-State Mining District to illustrate the impact of silicosis on the lives of area miners and their families. It was Dick who famously dubbed Treece, Kansas’s Main Street as the “street of walking death.” An estimated one hundred people stayed to watch the film in the Connor Hotel’s Empire Room. Evan Just decried the sixteen and a half minute film as a “smear campaign” against the mining district and the companies that operated there.
After twelve hours, Secretary Perkins was scheduled to leave Joplin to return east. She announced that she would “appoint in the near future a committee of representatives of the three states to explore the possibilities of perfecting a ‘state compact agreement’ for coordinating the work of concerned authorities and agencies.”
Before leaving, she spoke to a crowd of 700 to 800 people at an open labor meeting sponsored by the International Union of Mine, Mill, and Smelter Workers and the American Federation of Labor. Her speech focused on the need to improve housing and living conditions in the mining district. After concluding her remarks, Secretary Perkins then left to catch her train.
As David Rosner and Gerald Markowitz point out in their book, Deadly Dust, the issue of silicosis faded away because of the lack of a strong labor movement to press for better working and living conditions, and the subsequent collapse of the mining industry in the Tri-State region. After the death of FDR, subsequent administrations had little concern for miner’s lung. But for a brief period of time, Joplin and the rest of mining district captured the attention of the nation
Sources:Joplin Globe Deadly Dust: Silicosis and the On-Going Struggle to Protect Workers’ Health by David Rosner and Gerald Markowitz “What You Really Want Is an Autopsy”: Frances Perkins and the U. S. Government Conference in Joplin, Missouri, 1940 http://historymatters.gmu.edu/d/128/
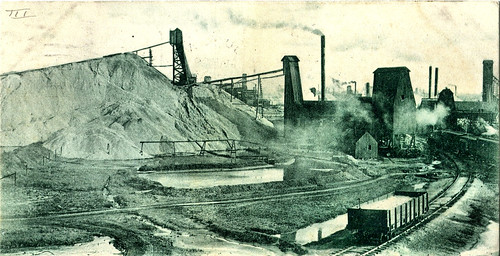
Perils of the Mines – Snapshot 1910
From the beginning, lead and zinc mining in the Joplin district was a dangerous means to make a living, and if lucky, a fortune, too. The year 1910 was considered a good one, respectively, when compared to 1909 when 51 miners lost their lives. In 1910, in contrast, only 32 miners were killed in the pursuit of the valuable ore. Every year, mine inspectors from the state toured the mines which surrounded Joplin to ensure compliance with mining laws and to note deaths and the causes behind them. In 1910, two inspectors toured 551 mines and 65 accidents. Here are the results and a snapshot of mining in Joplin in 1910.
In summary, the most dangerous element in a mine came from above. Of the combined deaths and serious injuries, falling mine roofs accounted for 27% of the victims. The next deadliest was the more obvious danger of explosives in the form of premature explosions, squib shot (involved in the dynamiting process), and to a degree, the foul air which was caused by failing to blow out the air in a mine following an explosion. Sadly, even entering and exiting a mine bore a certain amount of lethal danger, as our previous post on the unfortunate Number 52 noted.
Source: Joplin News Herald
No. 52
“No other Chinaman in Joplin has ever enjoyed the distinction of being the mixer that No. 52 was,” the Joplin News Herald remarked, recalling the life of one of the city’s few Chinese residents.
Little is known about “No. 52.” According to an article in the News-Herald, “No. 52” was the nickname of a Chinese immigrant named “Sam Wung, or something of a similar sound.” He was born the son of a fish vendor in Hong Kong. After he fell in love with the daughter of a well-to-do Hong Kong merchant, Sam sought to prove himself worthy of her love. Despite his best efforts, Sam failed to acquire the wealth he sought. So he boarded a ship for the United States, arriving in Louisiana, and found work at a cotton plantation.
Sam found himself working in cotton fields alongside African-Americans. It was also in Louisiana there that he obtained the nickname “No. 52.” “When payday came he received his envelope marked 52. And the title stuck with him.” A man named C.B. Oats met Sam in Louisiana and brought him to Joplin to find work in the mines. When a miner asked, “What’s the Chink’s name?” Oats replied, “They call him No. 52.” The name stuck.
Sam spoke wistfully of the girl he left behind in Hong Kong, but declared he could not return because a group of white men had cut off his queue while in Louisiana. Chinese men were required to wear their hair in a queue [pigtail] in deference to the emperor. If a Chinese citizen disobeyed this order, it was considered treason, and the penalty for disobedience was death. Fearful he would be executed if he returned to Hong Kong, Sam hoped to save up enough money to send for his beloved.
He found work in the mine of Monroe Clark and John F. Wise located on West Third Street just south of the Joplin Overall Factory near Byers Avenue. According to the News-Herald, Sam was the only Chinese immigrant to work in Joplin’s mines. It was explained that “Unlike his fellow yellow skinned brethren who contented themselves with cleaning dirty clothes and eating rice three times a day, No. 52 sought employment with white men, and despite his nationality he became a favorite.”
For “a number of years he labored with white men. Industrious, good natured, and honest, he won for himself an esteem that is seldom granted to Chinamen.” Impressed with Sam and his rapport with miners, John F. Wise offered him a position as a clerk in his grocery store, which Sam accepted. But even though he worked behind a counter, Sam would leave work in the evening to go to the mine and “spend many hours with the boys underground, chatting and telling stories.”
It was on one of these occasions that Sam stepped onto a tub to be lowered into the mine when tragedy struck. As the tub descended, the “can dropped suddenly a distance of fifteen feet, then stopped.” A cable had slipped on the whim [a whim was a large windlass]. Sam was jerked out of the tub and was “dashed to death” on the floor of the mine one hundred and thirty feet below. His broken body was retrieved and laid to rest in Fairview Cemetery. Sam’s grave was marked with a simple stone that read, “No. 52.”
His death brought sorrow to “hundreds of hearts for No. 52 was a popular Chinaman and he numbered his friends by his acquaintances.”
Source: Joplin News Herald
S.B. Corn Returns to Joplin
After having left Joplin 35 years earlier, S.B. Corn returned to the city in 1910, amazed by the city that had replaced the small hamlet he once knew. Upon his arrival, he inquired after several old-timers, including attorneys Clark Claycroft and Leonidas “Lon” P. Cunningham. Corn was saddened to find that both men had passed away. The only men still alive in Joplin that he knew from the 1870s were D.K. Wenrich and E.B. McCollum.
Corn was also disappointed to find that the spot where his smelting plant once stood in East Joplin could not longer be ascertained. He did, however, find the old building that once housed the Senate saloon. Unfortunately, the reporter accompanying Corn failed to report its location.
At one time, Corn allegedly owned several hundreds, if not thousands of acres in the Joplin area that extended south into Newton County. Over the years he sold the land off, most of it purchased by Joplin capitalist John H. Taylor. He built his first lead smelting plant in 1870 near the village of Cornwall (now called Saginaw). He built his next smelter closer to Joplin. It used air furnance fueled by wood. As Corn described it, “Hot blast, rushing over the ore, converted it into a molten mass which drained off into kettles. From these kettles it was ladeled out into moulds, and pigs, ranging in weight from 8/0 to 100 pounds, were formed. The metal was hauled over land to Baxter [Springs], Kansas, and shipped by railroad to St. Louis.”
According to the reporter, “Much of the ore smelted was produced from Mr. Corn’s land in the Kansas City Bottoms and was purchased from the lessees. The story is told that the smelting company sometimes paid for one load of lead five or six times, the operators being clever enough to have the same product weighed any number of times.” When this was discovered, duplicate sales were “abolished.” Corn eventually left Joplin and headed east to Pennsylvania where he engaged in the gas and coal business, but on a return trip west felt the urge to see Joplin once more.
He exclaimed, “When I was in there the seventies, there was no west Joplin. This part of the city was nothing but prairie. I feel like Rip Van Winkle, and can ahrdly realize that a city could have grown so rapidly as this one.”
Source: Joplin News Herald, 1910.
Mining – Progress and Prosperity
An illustration from the Joplin Globe invoking the spirit of progress that pervaded much of Joplin’s history.
Source: Joplin Globe
A Plunge Down a Sixty-Foot Shaft
Every day hundreds, if not thousands, of automobiles rumble through downtown Joplin. Most drivers go about their business without a thought that there may be empty mine shafts below their wheels. We here at Historic Joplin do — which is not to say we’re afraid of our vehicle plunging into a gaping chasm on Main Street, but in an area riddled with mine shafts, tunnels, and sinkholes, the ground giving way does happen from time to time. Mine shafts even presented a threat to folks, who despite having a familiarity with the dangers of working in the mines, had the misfortune to make a misstep. Or, in the case of James “Jim” T. Bodine, the wrong way home.
In the summer of 1904, Jim Bodine was on horseback herding the family cow home for the night. As he passed south of Twenty-Sixth Street, he had to ride through some brush when he and his horse unexpectedly encountered an abandoned mine shaft. Bodine, who was a, “well known and very popular mine superintendent and operator,” undoubtedly knew about mine safety, but riding your horse into a mine shaft in the middle of the night was something he had thought little about up to this point. Bodine’s horse pitched forward into the shaft. It managed to dig its forelegs into the mine shaft so that it seemed as if it would be able to get both itself and Bodine out of the shaft. Unfortunately, its legs buckled and the two plunged sixty feet into a water-filled mine shaft.

Abandoned mines poise significant danger risk in any mining area, such as this one located in California.
Both man and horse surfaced with Bodine still in the saddle. The horse struggled to keep its nose above the water. Bodine tried to sit in the saddle as long as he could, but realized the horse could throw him at any time, so he slipped into the water. His head throbbing from a bump to his head, Bodine managed to climb two or three feet onto the walls of the mine shaft. As the strength began to leave his arms, he began to cry for help. There he remained for over an hour yelling for help. In the water below Bodine, his horse was “plunging and striking his feet right and left.” Gritting his teeth, he sank his fingers “into the sides of the shaft as far as possible.”
Fortunately for Bodine, a Mrs. Carter was passing by when she heard his cries for help. She “ran to the shaft, shouted a word of encouragement to Mr. Bodine, and then ran for help.” Mrs. Carter brought James Ingram, D.E. Krokroski, and H. Dillon back to the mine shaft. There the three men lowered a rope to Bodine which he tied around his waist. Together the men pulled Bodine up to the surface where he was rushed home. Four doctors were summoned, but found that Bodine was in good shape despite his harrowing ordeal.
Bodine later told a Globe reporter, “There was a time when I thought I would have to give up and fall into the water. After Mrs. Carter looked into the shaft and then ran for assistance it seemed hours before assistance came. I felt my strength gradually giving away, and it seemed that every minute would be my last.” Even as the rope was being lowered to him, Bodine confessed, “I thought I would not e able to keep my position until I could get it tied, but it is remarkable how a man’s strength will stay by him when his life is at stake.” As for his horse, several men tried to extricate it, but as of the newspaper’s deadline, they had not been able to pull it out of the shaft.
Source: The Joplin Globe
Death in the Mines
Lead and zinc mining was the heart and soul of early Joplin. Men toiled in the mines to earn their living or, in many cases, meet their end. There were a variety of ways that death came to those who worked in the mines, often sudden and very violent.
On June 13, 1901, the Carterville Record reported that T. Hibler, a mining engineer working in nearby Galena, fell into a mine shaft over one hundred feet deep while walking to work at 5:30 a.m. Perhaps it was simply luck, or maybe the manner in which the unfortunate engineer tumbled downward into the darkness, but Hibler survived the fall. Not only did Lady Luck spare his life, but shortly after, a passerby came to his rescue. Amazingly, Hibler suffered only a few cuts, bruises, and a sprained ankle. He was one of the fortunate as others were not so lucky.
In James Norris’ “AZn: A History of the American Zinc Company” he noted that “In 1897 soaring prices and continued active demand produced large profits for miners in the Joplin zinc-ore district, and the following year was one of the most prosperous in the history of zinc mining.” This boom in lead and zinc mining attracted the attention of wealthy Eastern investors. In 1899, a group of Boston capitalists formed a corporation they called American Zinc, Lead, and Smelting Company. American Zinc, as it was commonly known, became one of the major players in the Tri-State Mining District.
In 1902, Harry S. Kimball was sent to Joplin to evaluate the company’s prospects in Joplin. He later recalled that Joplin was a, “bleak prospect for a tenderfoot to see as his first contact with a mining camp.” Hugh chat and slag piles littered the landscape. Miners were using “relatively simple and inefficient” mining methods. Thus men who were on the cusp of a century that heralded rapid technological and industrial innovations were operating as if they were still in the Dark Ages.
Historian Arrell M. Gibson describes the various mining techniques used in the Joplin area in his book, “Wilderness Bonanza.” Shafting, which required miners to create a vertical access shaft into the earth, was dangerous work. Miners drilled openings into the rock face and then inserted sticks of dynamite into the holes in order to break up solid rock. Dynamite, if handled incorrectly, was deadly. Miners sometimes had to tamp sticks into place. This involved tapping the explosive material into a firmer or deeper position. If they neglected to use a wooden stick to tamp in the dynamite, often using a metal bar instead, it could create sparks and cause a premature explosion with devastating effect.
Adding to the danger, miners also used giant powder, which was more powerful than regular black powder, to break up solid rock surfaces. Gibson states that many miners complained that giant powder caused headaches and nausea. But if a miner was fortunate enough not to die in a mine collapse, premature explosion, or suffocate, there was a good chance he would die early from silicosis. Silicosis is a condition caused by breathing in crystalline silica dust. After a controlled explosion, miners often failed to wet down the rock and as a result, inhaled minute particles of rock dust, which damaged their lungs like invisible razorblades piercing through their lung tissue. Miners who suffered from silicosis experienced shortness of breath, coughing, fever, and even a changing of the color of their skin. Of the many miners who eventually succumbed to the manufactured disease, one was Oscar C. Rosebrough. The thirty-six-year-old miner died of “miner’s consumption” in the summer of 1917.
Other deaths came suddenly and mercifully for some. The Carl Junction Standard reported on September 12, 1903, Walter McMahan was telling jokes and laughing with his coworkers at the Edith Mine near Joplin when a large boulder fell from the mine roof and crushed him. Meanwhile, The Carthage Evening Press recounted the death of Riley Marley, who was killed when he and his partner set off two shots of blast in a mine shaft. When one of the shots failed to go off, the two men reentered the mine to re-tamp the shot. As Marley tamped the shot back into place it exploded and drove the tamping rod through his head. He died instantly. His partner was blinded by the blast but survived.
Much of the danger came from simply entering the mines or processing areas. In 1905, Nathan Rice was struck on the top of his head by a falling timber. He later died of his injuries. In 1916, John Campbell was killed when he got caught in a drill rig. In 1882, Johnie Craig died when he went into a mine contaminated by bad air. In 1920, Kenneth Everett, a five year old child, died from bad air in an abandoned mine shaft.
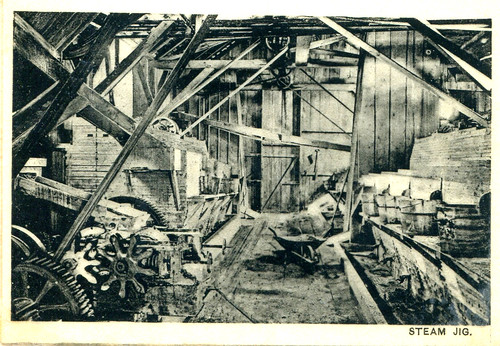
Far more complex than the hand jig, it's not hard to understand the danger of working around this steam powered jig.
Close calls were common and sometimes bizarre. In 1902, William Morgan was injured while working in the Big Six Mine when an icicle fell from the top of a mine shaft and hit him in the back. The icicle was heavy enough that it fractured his shoulder blade, but the physician who tended Morgan expected his patient to recover.
The zinc and lead of Joplin brought great wealth to some, work to many, and danger to all who entered the mines to retrieve it.
Sources: “Mine Accidents and Deaths In the Southwestern Area of Jasper County, Missouri, 1868-1906,” Volume I. Compiled by Webb City Area Genealogical Society. “Mine Accidents and Deaths In the Southwestern Area of Jasper County, Missouri, 1907-1923,” Volume II, “Accidents, Deaths, and Other Events.” Compiled by Webb City Area Genealogical Society. “Wilderness Bonanza” by Arrell M. Gibson